A solar battery system is an excellent choice for homeowners seeking energy independence and peace of mind. As demand for solar power grows, maximizing its potential to get the most out of your investment becomes increasingly important. Integrating a solar battery system into your home provides a reliable and efficient way to store excess solar energy for future use. This enhances energy self-sufficiency, reduces reliance on the grid, and saves on energy costs.
Benefits of a Solar System with Battery Backup
Adding a battery backup to your solar system offers numerous advantages, including:
- Reduced Electricity Bills: Storing and using your solar energy over time can significantly cut utility costs. A battery backup system also lets you take advantage of time-of-use (TOU) pricing by storing energy during low-rate periods and using it during peak-rate periods, optimizing energy expenses.
- Energy Independence: The ability to generate and store your electricity reduces dependence on the grid, giving you greater control over your energy usage.
- Power During Outages: A solar battery backup system ensures you have a reliable power source during outages, keeping essential appliances and devices running.
- Maximizing Solar Utilization: Stored solar energy can be used at night or during cloudy weather, allowing you to fully utilize your solar panel system.
- Increased Property Value: As renewable energy solutions gain attention and appeal, investing in a solar panel system with a battery backup can increase the value of your home.
- Environmental Benefits: Solar battery systems reduce reliance on fossil fuels, decrease carbon emissions, and contribute to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
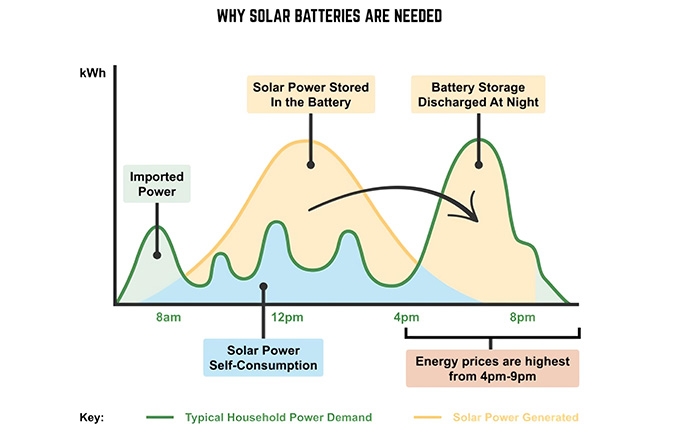
Key Considerations Before Choosing a Solar Battery Storage System
Before selecting a solar battery system, several factors should be considered to ensure it meets your needs. From understanding the difference between grid-tied and off-grid systems to evaluating battery types, these considerations provided by Home Power Inverter will help you make the right decision for your home and energy future.
1. Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid Systems
- Grid-Tied Systems: These systems connect your home to the utility grid, which provides electricity when your solar panels are not generating enough power. With grid-tied systems, solar energy powers your home first charges your batteries, and then exports any excess energy to the grid. Many regions offer net metering programs that provide utility credits for exported energy, further reducing your bills.
- Off-Grid Systems: These systems operate independently of the utility grid and rely entirely on solar energy, batteries, and backup generators. While off-grid systems provide complete energy independence, they require higher upfront investment and extensive planning to meet 24/7 energy needs. Additionally, they demand robust battery storage and backup solutions to ensure consistent power, especially during emergencies or at night.
2. Whole-Home vs. Partial Backup
- Whole-Home Backup: Ideal for those with a larger budget, whole-home systems provide power to all appliances during outages, offering a seamless user experience. This is especially useful for homes with significant energy demands or critical medical equipment.
- Partial Backup: A more economical option, partial backup systems prioritize essential devices during outages. This is achieved by setting up a sub-panel dedicated to key appliances, creating a cost-effective yet reliable energy solution.
3. Types of Solar Batteries
- LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate): Known for safety, long lifespan, and heat resistance, LFP batteries are ideal for residential and industrial storage systems.
- NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt): Offering higher energy density, NMC batteries are more compact, making them suitable for portable devices and electric vehicles. However, they are less durable under high temperatures compared to LFP batteries.
- SLA (Sealed Lead-Acid): A cost-effective choice, SLA batteries are heavier, have lower energy density, and have a shorter lifespan. They are typically used in uninterruptible power supplies (a UPS inverter) and small off-grid applications.
Why LFP Batteries Are Popular: LFP batteries have emerged as a favorite for storage applications due to their affordability, superior safety features, long-lasting performance, and thermal stability.
Key Factors to Consider When Buying a Solar System with Battery Backup
When choosing components for a solar battery backup system, keep the following factors in mind:
Capacity: Battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), indicates the amount of energy a battery can store. However, not all stored energy is usable. Depth of Discharge (DoD) refers to how much energy can be discharged without damaging the battery. Lead-acid batteries typically have a DoD of around 50%, while LFP batteries offer a higher DoD of about 90%, maintaining longevity even with deeper discharges.
Cycle Life: LFP batteries are renowned for their impressive cycle life, enduring between 2,000 and 10,000 charge-discharge cycles depending on manufacturer, quality, and usage conditions. Proper maintenance and adherence to usage guidelines can optimize cycle life and ensure years of reliable performance.

Voltage: Low-voltage batteries (≤100V) typically operate at 48V, these batteries are easier to install and upgrade but provide slower discharge rates. They are ideal for off-grid applications but may struggle with high-demand appliances. High-voltage batteries (≈400V) rated at around 400V, high-voltage systems can manage higher energy loads, charge and discharge faster, and are suitable for homes or businesses with significant energy demands.
Inverter Compatibility: Adding batteries to an existing solar system requires an inverter that supports battery integration. Battery-ready inverters ensure seamless energy management between solar panels, batteries, and home energy loads, optimizing performance and efficiency.
Technical Support: Choose a solar battery supplier that offers robust technical support to ensure a smooth experience throughout installation, setup, and operation. Reliable support ensures peace of mind and maximizes the return on your solar and storage investment.
Conclusion
Investing in a solar system with a battery backup offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, energy independence, and enhanced property value. By understanding the different system types, battery options, and essential considerations, you can choose a solution tailored to your needs. With the right setup, you’ll not only reduce your environmental footprint but also gain reliable, sustainable energy for years to come.
