Pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters are two common types of inverters. They have some differences in working principle, performance characteristics, application field, waveform, and compatibility. Next, we will explain the differences between pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters in various aspects.
Pure sine wave inverter
A pure sine wave inverter refers to an inverter whose output current waveform is completely consistent with a sine wave. It can convert the power of a DC power supply (such as a battery or solar cell) into AC power to provide stable AC power for home, commercial, and industrial equipment. The output current waveform of a pure sine wave inverter is of high quality and can achieve low harmonic distortion when interfaced with a grid power supply.
Modified sine wave inverter
The modified sine wave inverter is an inverter whose output current waveform is close to a sine wave, but compared with the pure sine wave inverter, its current waveform has a certain distortion. The modified sine wave inverter realizes waveform control by controlling the conduction and cut-off time of switching elements such as thyristors and transistors.
Differences between pure sine wave inverter and modified sine wave inverter
Waveform Quality
- Pure sine wave inverter: It produces a smooth, continuous waveform that closely resembles the AC power provided by the utility grid. The waveform is a true sine wave with a smooth and rounded shape.
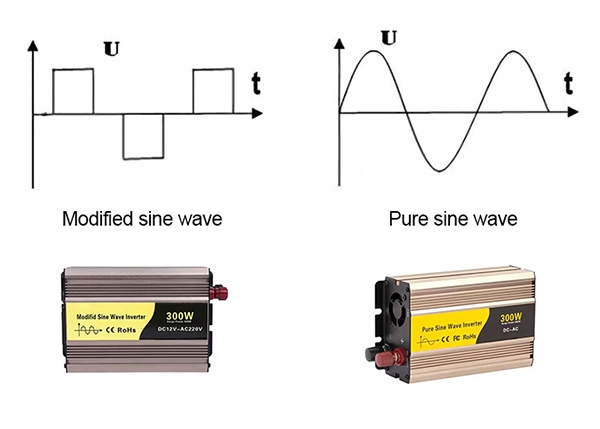
- Modified sine wave inverter: It produces a waveform that is more like a stepped approximation of a sine wave. The waveform has a blocky, stepped shape that is less smooth and closer to a square wave.
Compatibility with devices
- Pure sine wave inverter: It is compatible with almost all AC devices, especially those with sensitive electronics or motors. Devices such as computers, refrigerators, microwave ovens, and medical equipment require the clean power provided by a pure sine wave inverter. Due to its high waveform quality, it is suitable for all types of electronic devices and loads, including the most sensitive appliances such as computers, medical equipment, precision instruments, etc. It is also suitable for connecting to the grid as an interface for distributed generation systems such as solar power generation.
- Modified sine wave inverter: It is suitable for many basic devices, and loads that do not require high waveform quality, such as incandescent lamps, electric heaters, simple power tools, old appliances, and lighting equipment. These devices are not very sensitive to waveform changes in voltage and current, so they can work well on modified sine wave inverters. However, it may not be suitable for equipment with sensitive electronic equipment, inductive loads (such as motors), or audio/video equipment. These devices may operate inefficiently, make noise, or not work at all.
Efficiency and Power Consumption
- Pure sine wave inverters: Pure sine wave inverters are generally more efficient at converting DC to AC, resulting in less wasted energy and lower heat output. The smooth waveform ensures that devices operate at the expected efficiency.
- Modified sine wave inverters: Modified sine wave inverters are less efficient due to the stepped waveform, which can cause devices to consume more power than necessary. The power inverter itself may also generate more heat.
Price
- Pure sine wave inverters: They are generally more expensive due to the complex electronics required to produce a true sine wave. The higher cost is often due to better performance and wider compatibility.
- Modified sine wave inverters: Modified sine wave inverters are lower priced, making them a more affordable choice for basic applications that don't require high precision in power output.
Performance
- Pure sine wave inverters: Pure sine wave inverters provide smooth, reliable power, which is critical for devices that require precise voltage and frequency regulation. It ensures that sensitive electronic devices and appliances operate properly without risk of damage.
- Modified sine wave inverters: Modified sine wave inverters may cause problems with some devices, such as increased noise in audio equipment, erratic behavior of electronic devices, or reduced motor efficiency. Some devices may overheat, malfunction, or have a shortened life when powered by a modified sine wave inverter.
