In the field of renewable energy, solar energy, as a clean and pollution-free form of energy, is gradually becoming a crucial direction for global energy structure transformation. Solar generators, as key equipment for harnessing solar energy, have garnered significant attention regarding their working principles, technological composition, and application areas. This article will explore in-depth the definition, working principles, structural components, technical characteristics, and application prospects of solar generators, aiming to provide a comprehensive and profound understanding.
What is a Solar Generator?
Firstly, Inverter.com will briefly talk about the definition of a solar generator. A solar generator is a power generation system that directly converts sunlight into electrical energy through solar panels and manages and stores the energy via power electronics equipment. It can power appliances like DC energy-saving lamps, radios, and televisions. It can also be converted into AC power via an inverter to meet broader electrical needs. Solar generators play a vital role in independent power supply, remote area power supply, urban photovoltaic grid-connected power generation, and other fields due to their unique advantages.
How does a Solar Generator Work?
The working principle of a solar generator is primarily based on the photovoltaic effect of semiconductors. When sunlight hits the solar panels (mainly composed of semiconductor materials like crystalline silicon), photons interact with the electrons in the semiconductor material, creating electron-hole pairs. Under the influence of the electric field in the P-N junction, the electrons and holes move in opposite directions, forming a current. In this process, light energy is directly converted into electrical energy without the need for intermediate steps like thermal energy, thus offering high conversion efficiency.
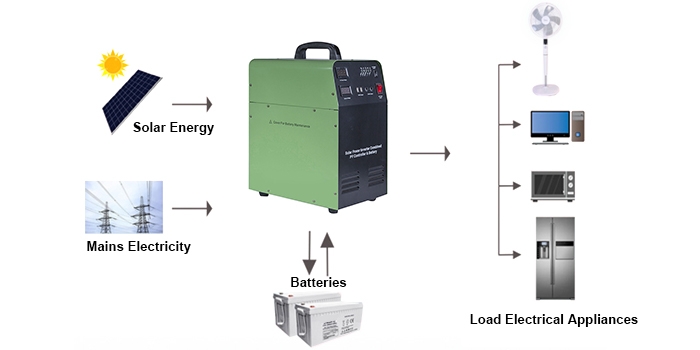
What are the Structural Components of Solar Generators?
A solar generator consists of several key components, including solar cells, charge and discharge controllers, inverters, batteries, testing instruments, and computer monitoring power electronics equipment.
- Solar Cell Modules: These are the core components of a solar generator, composed of multiple solar cells connected in series or parallel, used to convert sunlight into DC power. The performance of the solar cell modules directly impacts the efficiency and stability of the entire power generation system.
- Charge and Discharge Controllers: These solar charge controllers manage the charging process from the solar cells to the batteries, preventing overcharging, over-discharging, and short-circuiting. They also automatically adjust the charging current and voltage based on the battery's state, ensuring optimal performance.
- Inverters: A critical device in solar generators, inverters convert the DC power generated by the solar cells into AC power to meet the needs of household appliances and the grid. Inverters offer advantages such as voltage stability, low waveform distortion, and high conversion efficiency.
- Batteries: Batteries serve as the energy storage devices in a solar generator, storing the power generated by the solar cells and supplying power to loads during periods without sunlight or during grid outages. Common types include lead-acid batteries and lithium batteries, each with different capacities, lifespans, and costs.
- Testing Instruments and Computer Monitoring: These devices are used for real-time monitoring of the solar generator’s operational status and power generation efficiency, including measurements and records of voltage, current, and power. The computer monitoring system allows users to remotely monitor the generator's operation, enabling timely detection and resolution of faults.
Technical Characteristics of Solar Generators
Solar generators possess various technical characteristics that make them widely applicable in the energy sector.
- Clean and Pollution-Free: Solar generators utilize solar energy for power generation without consuming fossil fuels or emitting greenhouse gases or harmful substances, making them clean and pollution-free.
- Renewable Energy: Solar energy is an inexhaustible renewable resource. As long as the sun exists, solar generators can continuously generate power to meet electricity demands.
- High Flexibility: Solar generators can operate independently, unaffected by geographic location. Their scale can be adjusted to fit different scenarios, making them suitable for various power generation needs.
- High Safety: Solar generators have no moving mechanical parts, no noise, and no vibration, offering high safety and reliability. They also include protection features such as overcharge, over-discharge, and short-circuit protection to ensure safe operation.
- Significant Economic Benefits: With the ongoing development and maturation of solar technology, the manufacturing cost of solar generators is decreasing, and their efficiency is increasing. In areas with abundant sunlight, solar generators offer significant economic benefits, potentially saving users substantial electricity costs.
Application Areas of Solar Generators
Solar generators are used in a wide range of areas, including the following:
1. Independent Power Systems: In remote areas, unpowered regions, or areas not covered by the grid, solar generators can serve as independent power systems, providing electricity to residents. These areas often have poor transportation and weak power infrastructure, making traditional power supply methods difficult. Solar generators, with their high flexibility and easy installation, effectively solve these issues.
2. Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Power Systems: In urban areas and regions with good grid coverage, solar generators can operate in conjunction with the grid, sending excess power to utility companies for sharing and redistribution. This method not only reduces users' electricity costs but also lessens dependence on traditional energy sources and reduces environmental pollution.
3. Transportation and Urban Lighting: Solar generators can also be applied in transportation and urban lighting, such as solar electric vehicles and solar streetlights, which can be charged and powered by solar generators. These applications reduce traditional energy consumption and environmental pollution while enhancing the efficiency and reliability of vehicles and lighting systems.
4. Industrial and Commercial Sectors: In the industrial and commercial sectors, solar generators provide clean energy support to businesses and factories. By installing solar power systems, companies can reduce electricity costs, lower carbon emissions, and improve energy efficiency. Additionally, solar power systems can be combined with energy storage devices to ensure a stable power supply for enterprises.

Future Prospects
As global energy structures shift and renewable energy technologies continue to develop, solar generators are poised for broader growth in the future. Innovations and advancements are expected in the following areas:
1. Improving Photovoltaic Conversion Efficiency: Researching new solar cell materials and optimizing solar panels and cell structures to improve the photovoltaic conversion efficiency of solar cells will be a key development direction. This will help reduce manufacturing costs and improve the efficiency of solar generators.
2. Reducing Manufacturing Costs: As production scales up and technology advances, the manufacturing cost of solar generators will gradually decrease, making them more accessible and affordable, thus providing clean energy support to more people.
3. Intelligence and Automation: Future solar generators will become more intelligent and automated. By integrating IoT, big data, and AI technologies, they will offer remote monitoring, intelligent scheduling, and fault prediction, improving operational efficiency and reliability.
4. Diverse Application Scenarios: With continuous technological progress and expansion into new fields, solar generators will be applied in more diverse scenarios. Beyond traditional independent power systems and photovoltaic grid-connected power systems, solar generators will see widespread use in agriculture, transportation, construction, and more.
As a vital piece of equipment for solar energy utilization, solar generators offer numerous advantages, including being clean and pollution-free, utilizing renewable energy, providing high flexibility, ensuring safety, and delivering significant economic benefits. In the context of global energy transformation and ongoing advancements in renewable energy technologies, solar generators have a promising future. We look forward to more breakthroughs and progress in areas such as technological innovation, cost reduction, intelligence, and diverse applications, contributing more to sustainable development for humanity.
