As a vital component of modern power electronics, inverters play an indispensable role in various power systems. Their importance is particularly pronounced in off-grid solar power systems. Today, Home Power Inverter will delve into the specific applications, functions, and significance of inverters within off-grid solar systems.
Fundamental Concepts of Off-Grid Solar Electric System
Before understanding the role of inverters in off-grid solar power systems, it's crucial to clarify the concept of "off-grid." An off-grid solar system operates independently of the national grid. It typically combines battery energy storage with an inverter to form a self-sufficient electricity supply. These systems are particularly suitable for remote areas, places without grid coverage, or sites requiring independent power, such as islands, mountainous regions, field operation bases, and industrial and commercial facilities.
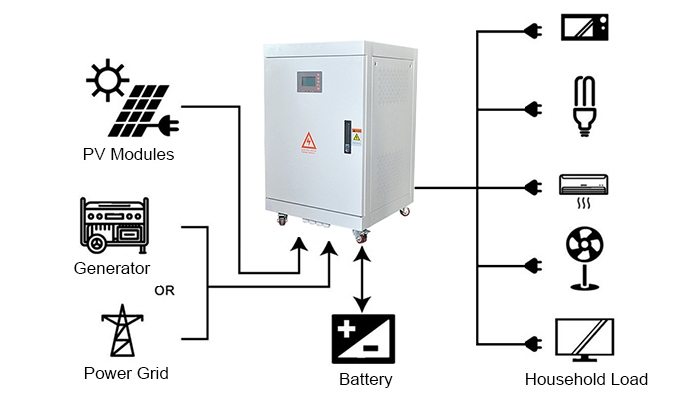
Principles and Types of Inverters
An inverter is a power electronic device whose primary function is to convert direct current (DC) power into alternating current (AC) power. It typically consists of an inverter bridge, control logic, and filtering circuits. The core function of an inverter is to convert low-voltage DC power (e.g., 12V, 24V, or 48V) into the AC power required by household and industrial systems.
Inverters can be classified into various types depending on their applications and requirements. In off-grid electrical systems, the most common types include pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters:
- Pure sine wave inverters: Produce an output waveform identical to utility-grade electricity, suitable for sensitive equipment requiring high power quality, such as precision instruments and household appliances.
- Modified sine wave inverters: Offer a less refined waveform and are more cost-effective, making them suitable for devices with lower power quality requirements, such as lighting and power tools.
Core Functions of Inverters in Off-Grid Solar Power Systems
In off-grid solar power systems, inverters perform several essential functions:
- DC-to-AC Conversion: The primary role of an inverter is to convert stored DC power from batteries into AC power to meet the demands of household and industrial devices. Since most appliances are designed to operate on AC power, the inverter serves as a bridge, making DC power usable.
- Voltage Matching and Regulation: Inverters match and regulate system voltage. The battery voltage must align with the inverter’s input voltage. Through precise control logic, the inverter ensures stable and reliable output voltage, facilitating the smooth operation of the entire power system.
- Output Power Management: Managing output power is another key function of inverters. Output power is typically expressed as apparent power (VA) or active power (W). For example, a 500VA inverter with a power factor of 0.8 delivers an active power output of 400W. The inverter adjusts output power flexibly based on varying load demands, ensuring stable operation.
- Peak Power Support: Inductive loads like air conditioners and water pumps require higher startup power, often 3–5 times their rated power. Inverters provide the necessary peak power during startup, aided by internal storage components such as capacitors and inductors. This ensures the smooth startup and operation of such devices.
- Improving System Efficiency: Conversion efficiency is critical to the overall performance of the off-grid system. The efficiency of inverters typically ranges between 80% and 90%, depending on factors such as circuit design and battery type. High-frequency isolation is more efficient than low-frequency isolation, and systems with higher operating voltages also tend to be more efficient. Thus, selecting the right inverter and battery involves balancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Automatic Switching and Protection: Many inverters feature automatic switching functions. For instance, when battery power is insufficient, the inverter can automatically switch to grid power to maintain continuous supply. Advanced inverters also include protections against overvoltage, undervoltage, and short circuits, safeguarding both the power system and connected devices.

Applications of Inverters in Off-Grid Solar Power Systems
Inverters are widely used across various domains, including residential, industrial, and commercial applications.
- Residential Backup Power Systems: In residential setups, inverters are often combined with batteries and solar photovoltaic panels. During grid outages, the inverter converts stored DC power into AC power to supply household appliances, ensuring uninterrupted power and a normal lifestyle.
- Industrial Automation Systems: In industrial settings, motor drives extensively use inverters. By adjusting output voltage and frequency, inverters enable precise speed and operational control of motors, enhancing productivity and reducing energy consumption. They also ensure a stable power supply for automated systems.
- Commercial Power Solutions: Facilities like hotels, hospitals, and data centers prioritize power reliability. Inverters provide dependable backup power during outages and improve power quality, protecting sensitive equipment from damage.
- Power Supply for Remote Areas: In remote areas where grid extension is challenging or costly, off-grid solar power systems with inverters are the primary power solution. Inverters convert DC power generated by solar modules or wind turbines into AC power, providing reliable electricity while promoting renewable energy utilization.
Conclusion
Inverters play a crucial role in the off-grid solar electric system. Beyond converting DC to AC power, they ensure voltage regulation, output power management, peak power support, enhanced efficiency, and protection mechanisms. Widely applied across residential, industrial, and commercial sectors, inverters provide reliable power supply and system security. With ongoing technological advancements, inverters are becoming more efficient, intelligent, and modular, contributing significantly to renewable energy adoption and smart grid development.
